Zynq
AMD Zynq is a System-on-chip (SoC) platform that combines an ARM CPU core with programmable logic. The CPU core (PS) and the FPGA (PL) are connected via AXI interfaces and allow for both the flexibility of a true CPU core (e.g. for Ethernet connectivity) and the power/performance advantages of an FPGA.
Architecture
The Zynq chip integrates two distinct processing systems: the Processing System (PS) and the Programmable Logic (PL). The PS is based on an ARM Cortex processor, offering high processing power and flexibility. In contrast, the PL is an FPGA fabric that allows for custom hardware development. The seamless interface between the PS and PL enables users to design systems that leverage both the software programmability of the PS and the hardware adaptability of the PL, making Zynq a versatile platform for a wide range of applications.
Connecting PL and PS
The image below shows how the AXI-Stream connection is built between PL and PS.
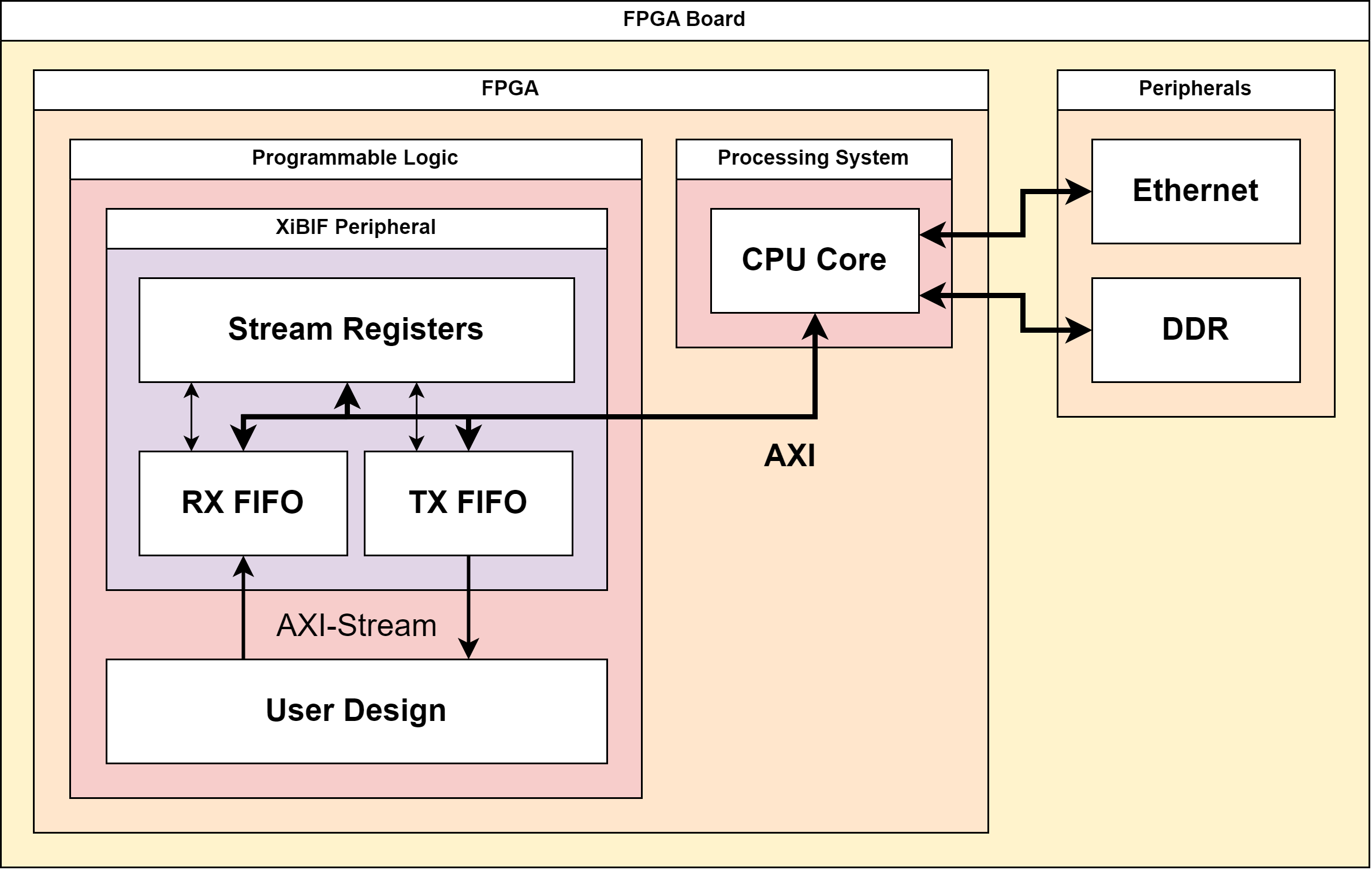
In both directions, the AXI-Stream is sourced or sunk from/into a hardware FIFO. The FIFOs announce their status in the stream registers, where the PS can react accordingly. The data from the FIFOs is then read/written from/to over a standard AXI-Lite bus. On the PS side, the stream data is stored in the DDR RAM (double data rate random-access memory).
The reason for the hardware FIFOs to exist is that the CPU core has many tasks to tend to. Inserting the hardware FIFOs thus allows continuous writing while the CPU only transfers this data from time to time.